Accredited Lean Six Sigma Certifications
Fix What Frustrates. Improve What Matters.
Every day, good people waste time fixing the same problems. Our courses help you break that cycle—whether you’re just starting out or leading system-wide change. Learn to see work differently, fix what slows it down, and build confidence.
These aren’t just courses—they’re problem-solvers, confidence-builders, and change-enablers for today’s complex, tech-powered workplaces.
One system. Three levels. Your journey.
White Belt : Awareness & Mindset
Discover how to spot everyday inefficiencies, reduce delays, and make simple, effective improvements—while strengthening your ability to improve how work gets done and contribute in more meaningful ways. This beginner-level certification builds your confidence to fix what's not working—without needing a new title or fancy tools.
Perfect for: Anyone new to Lean, looking to improve how work gets done.
Yellow Belt: Structured Problem Solving
Move from awareness to action. pply structured methods like DMAIC. Solve what slows work down—and deliver measurable results. Use practical tools to reduce waste and make everyday work better..
Perfect for: Early-stage changemakers ready to make measurable impact.
Green Belt: Lead Change, Coach Others
Step into a leadership role in improvement. Coach others, navigate complexity, and lead change that aligns with business strategy. Green Belt prepares you to guide teams, drive cross-functional projects, and make improvement stick
Perfect for: Professionals ready to lead meaningful, system-level change
How it all connects:
What Learners are saying
Not sure where to start?
Every improvement journey begins with one small change. Make yours today.
 Why join?
Why join?
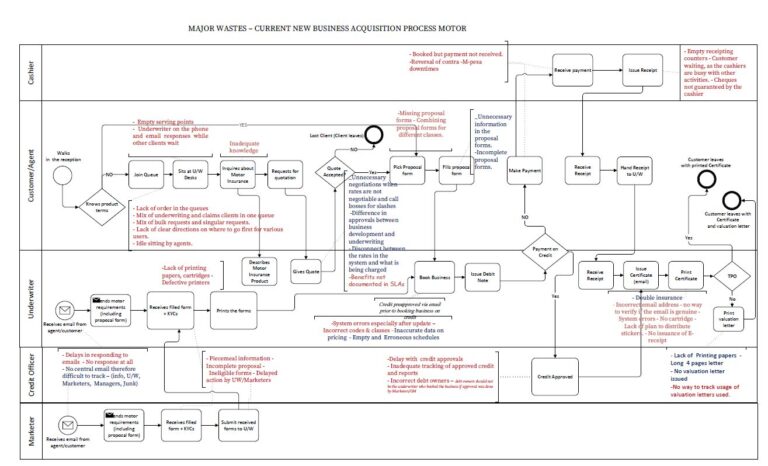
 Understand the 9 Lean wastes (TIMES EDGE) that slow down service and tech work.
Understand the 9 Lean wastes (TIMES EDGE) that slow down service and tech work. Learn through real-world examples you can relate to immediately.
Learn through real-world examples you can relate to immediately. Build a shared language with your team to identify and reduce waste.
Build a shared language with your team to identify and reduce waste. Walk away with practical steps you can apply the same day.
Walk away with practical steps you can apply the same day. Perfect for:
Perfect for: Quick Course—Lasting Impact
Quick Course—Lasting Impact Lean Banking Essentials
Lean Banking Essentials Customer Effort & Flow — Surface where customers and teams feel friction.
Customer Effort & Flow — Surface where customers and teams feel friction. Lean Foundations for Banking — Why waste reduction matters (Muda, Mura, Muri).
Lean Foundations for Banking — Why waste reduction matters (Muda, Mura, Muri). Apply the 9-Wastes Lens — Use the TIMES EDGE perspective across onboarding/KYC, underwriting, payments, servicing, and digital/branch ops.
Apply the 9-Wastes Lens — Use the TIMES EDGE perspective across onboarding/KYC, underwriting, payments, servicing, and digital/branch ops. Impact & Metrics — Tie fixes to turnaround time, rework, risk, and Customer Experience.
Impact & Metrics — Tie fixes to turnaround time, rework, risk, and Customer Experience. Wrap-Up & Assignment — Apply the method to your own workflow and earn a certificate.
Wrap-Up & Assignment — Apply the method to your own workflow and earn a certificate. What You’ll Gain
What You’ll Gain Faster detection of bottlenecks and handoff delays.
Faster detection of bottlenecks and handoff delays. Tools to prioritize fixes with data and customer effort.
Tools to prioritize fixes with data and customer effort. A recognized certificate of completion to strengthen your profile.
A recognized certificate of completion to strengthen your profile. Analyze. Improve. Perform.
Analyze. Improve. Perform.